Back to blog
Adaptive MFA: A smarter approach to authentication security
Auth & identity
Sep 25, 2024
Author: Alex Lawrence

In today's busy digital ecosystems where both UX and security are paramount, it's crucial to match your security responses to the appropriate threat levels at play so as not to disturb the user experience.
Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an advanced security method that uses contextual information and business rules to determine which authentication factors to apply to a user in a given situation. This article explains what adaptive MFA is, how adaptive authentication works, why it’s vital for strong identity security, and what comprises a best-in-class adaptive MFA solution in the rapidly evolving AI-powered era.
Understanding adaptive MFA
Adaptive MFA dynamically adjusts authentication requirements based on contextual factors like device type, IP address, and user behavior to balance strong security with a seamless user experience. By stepping up (increasing) or stepping down (reducing) the authentication process depending on the user's context, adaptive MFA allows trusted devices to log in with minimal friction, while adding extra layers of security for unfamiliar or suspicious activity. This flexibility lets organizations tailor authentication strategies to each device that attempts to log into their applications, ensuring robust protection while enhancing the user experience.
The shortcomings of traditional MFA
Traditional MFA can create unnecessary friction through enforcing the same security requirements for all users, regardless of their individual risk profiles. Every user must complete a secondary authentication step, such as entering a code from a mobile app or receiving a one-time password (OTP) via SMS. While this approach adds a layer of security, it can frustrate legitimate users by requiring them to perform extra steps during each login, even if they are using a familiar device or logging in from a trusted location.The blanket approach of traditional MFA also fails to account for varying levels of risk and can frustrate users who face repetitive and unnecessary challenges, leading to a poor user experience. Moreover, traditional MFA can be less effective at stopping more modern, advanced attack vectors, as it doesn’t adapt to emerging risks in real-time. If an attacker manages to compromise a user’s credentials and obtain access to their second factor (e.g., through phishing or SIM swapping), traditional MFA might not provide adequate protection, as it doesn't dynamically adjust based on suspicious behavior or unusual login contexts. Ultimately, the rigid, one-size-fits-all approach of traditional MFA can undermine both security and UX.
Adaptive MFA in action
Here’s a few examples of the types of user behaviors or indicators that might be interpreted as a trusted user vs a suspicious user in the eyes of adaptive MFA when logging into an app:
Trusted user: A user logs in from their home device during regular business hours. The system recognizes the device and location as consistent with their previous login patterns. Because the risk is low, adaptive MFA allows the user to access the app with just their password, streamlining the login process and reducing unnecessary friction. The user enjoys a smooth and efficient experience, quickly accessing the application without additional authentication steps.
Suspicious user: A login attempt is made with the correct username and password but using an unfamiliar device with a different operating system than the user typically uses. The adaptive MFA system detects that the login attempt is from a new device and that the browser's or device’s characteristics doesn’t match the user’s usual profile, such as indicating an outdated browser version or an operating system they have never logged in from before. These inconsistencies trigger a higher risk score. In response, the system steps up the authentication requirements, prompting the user to verify their identity through a second factor, such as entering a one-time password (OTP) sent to their email or performing biometric verification. If the user fails to complete these additional steps through consecutive login failures, consecutive login attempts, or if the system detects further anomalies (e.g., the browser environment appears manipulated or tampered with), access is denied.
How adaptive MFA works
Adaptive MFA is about creating rules that use contextual data to determine when to challenge a user with additional authentication steps. These rules can be as simple as a denylist of forbidden attributes (e.g., certain countries, device types, or public IP addresses) or as complex as a dynamic risk matrix that evaluates multiple factors in real time. Developers have the flexibility to define the "adaptive" mechanism based on their security needs, whether through a decision flow chart, cumulative risk scoring, or hard coded allow/deny lists.
The system continuously assesses various factors, such as geographical or physical location, registered devices, user roles, IP address, browser type, software versions, time of login, attempted action, and operating system. Each login attempt is evaluated against these criteria, with decisions made based on predefined rules or real-time risk assessments.
Here are a few examples of adaptive MFA rules:
- If a login attempt comes from an unusual location or an unrecognized device, prompt the user for additional verification.
- A user logging in from a trusted device or secure corporate network might only need to enter their password, while a login attempt from a public Wi-Fi network triggers an MFA challenge.
- If the system detects high-risk behavior, such as an unusual browser version or an inconsistent device fingerprint, it requires additional authentication steps like a one-time password (OTP) or biometric verification.
By allowing developers to tailor these rules to their specific security needs, adaptive MFA can provide a more flexible and efficient approach than traditional MFA. It can seamlessly adjust to each unique login scenario, offering strong protection without unnecessary friction.
Key benefits of adaptive MFA
Ultimately, adaptive MFA leverages contextual insights to deliver a secure, user-friendly authentication experience that adapts in real-time, keeping both security and usability in balance. It improves an organization's security posture while also supporting user productivity.
- Improved security: Adaptive MFA enhances enterprise security by continuously assessing risks during login attempts and adjusting authentication requirements accordingly. This dynamic approach adds layers of protection based on real-time risk assessments, making it difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even with compromised credentials. By customizing security measures to the assessed risk level, Adaptive MFA ensures that high-risk scenarios are met with stronger defenses, protecting business applications and data effectively.
- Better productivity: Adaptive MFA improves productivity by reducing the friction of traditional MFA systems. Users logging in from recognized devices or during regular hours face fewer authentication challenges, allowing faster access to applications and data. By intelligently assessing login risks, adaptive MFA minimizes unnecessary authentication steps, enhancing user convenience and streamlining workflows, which boosts overall efficiency within the organization.
These benefits are further amplified by advances in AI and machine learning, which enable systems to make real-time decisions and respond rapidly with the required step up or down to increase, or reduce, login friction.
Best practices in modern Adaptive MFA
Effective adaptive MFA starts with a strong baseline MFA solution that uses a combination of authentication factors, such as something you know (password), something you have (passkey), and something you are (biometric). If one factor is compromised, the overall security remains intact.Best-in-class adaptive authentication solutions monitor user behavior over time, establish baseline profiles, and flag anomalies. This allows the system to assign risk scores to suspicious events and adjust authentication factors in real-time.
Dynamic access policies
To establish baseline profiles for users, dynamic access policies are created using contextual information to determine user access and access management authentication factors. Each time a user attempts to authenticate, the request is evaluated and assigned a risk score based on the established user profile, which includes information such as location, registered devices, and user role. This dynamic assessment allows the system to adapt in real-time, supporting seamless, secure authentication that can evolve with a business’ changing needs.
Single sign-on
Integrating Single Sign-On (SSO) with adaptive MFA further helps streamline authentication. SSO allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, simplifying the login process and reducing the need to remember multiple passwords. When combined with adaptive MFA, it adds an additional layer of security by vetting each login attempt before granting access. Adaptive MFA can be easily integrated with existing SSO solutions.
MFA and Device Fingerprinting from Stytch
Adaptive MFA is only as effective as the quality of its data. Without accurate, comprehensive information about users, devices, and environments, even the most sophisticated adaptive MFA rules can fall short. Poor data quality can lead to false positives, unnecessary friction, or, worse, security gaps.
Stytch Device Fingerprinting (DFP) collects fine-grained device-related data, allowing you to build more accurate user profiles and confidently distinguish between legitimate users and potential threats. The solution enhances adaptive MFA by offering precise and reliable returning user identification. For developers and businesses alike, this combination results in a more seamless user experience without sacrificing security. By utilizing Stytch's DFP as part of your MFA flow, you can confidently reduce friction for legitimate returning users while dynamically increasing friction for potential bad actors.
This approach not only minimizes the drop-off that can occur when users face unnecessary MFA challenges but also ensures that unauthorized users cannot gain access, even with stolen credentials, unless their device passes the DFP check. For developers focused on growth and user conversion, adaptive MFA with Stytch’s DFP can help retain users by providing a login experience that feels secure yet unobtrusive.
Stytch's advanced browser deception detection capabilities provide a strong foundation for future security enhancements, with AI and ML at the backbone. With this combination of cutting-edge technology and seamless integration in to your existing systems, we can confidently claim we have one of the most powerful adaptive MFA solutions around.
Open-source example app with adaptive MFA
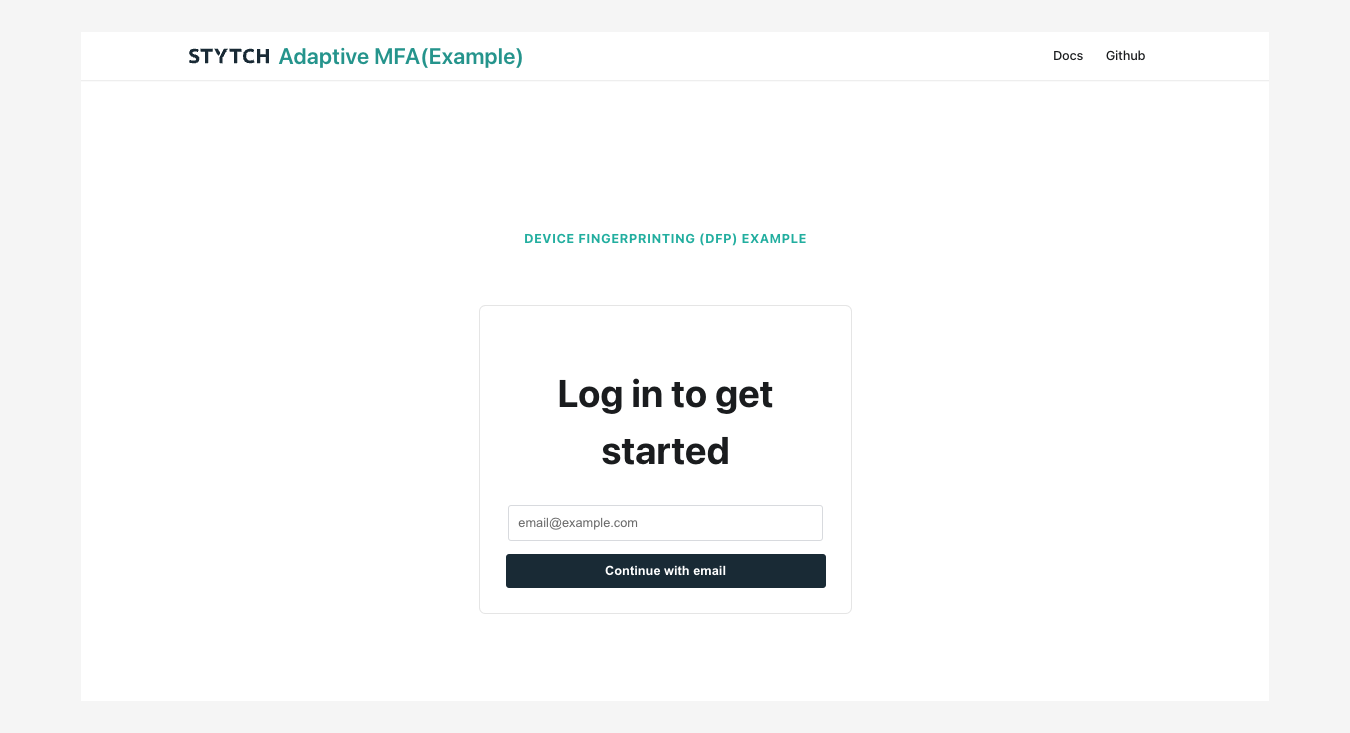
For developers, we have an open-source example app that demonstrates how to leverage Stytch's Device Fingerprinting (DFP) product to power adaptive MFA, where users are only required to complete MFA if they are logging in on a new device.
Clone the repo on GitHub to see the code in action.
To learn more about Stytch's Fraud & Risk Prevention solutions, get in touch with an auth expert today, or create an account to get started.
Stytch Fraud & Risk Prevention
Pricing that scales with you • No feature gating • All of the auth solutions you need plus fraud & risk
Authentication & Authorization
Fraud & Risk Prevention
© 2025 Stytch. All rights reserved.