Back to blog
Stytch Embedded Auth vs. Auth0 Universal Login
Auth & identity
Nov 1, 2024
Author: Ashley Weaver
Author: Basia Sudol
Author: Stytch Team

Designing an effective authentication experience is crucial for ensuring both security and a seamless user journey. One of the key implementation decisions you'll make is choosing between an embedded authentication or universal login architecture.
In this article, we'll explore what each method entails, highlight the key differences, and help you determine which approach is best suited for your needs.
Let's dive in.
What is Universal Login?
Universal login, also known as hosted login or authentication, is an approach that redirects users away from your site or application. Users are taken to the authentication provider’s domain in order to complete authentication flows like login, signup, or password resets. Once the user has successfully authenticated, they are redirected back to your site, the original domain.
This approach relies heavily on the external auth provider to handle the entire authentication flow and for security. While this works for some who need a simplified or an “out-of-the-box” setup, universal login often sacrifices user and developer experience by design since it effectively strips developers of any native in-app code control over the auth flow.
Auth providers like Auth0 encourage developers to implement universal login as their primary solution for authentication.
What is Embedded Authentication?
Embedded authentication, on the other hand, allows users to authenticate directly within your application without being directed. Users can complete the login, signup, or password reset process from your application or website. The authentication logic and components are embedded natively, providing an authentication experience where users never leave your site.
Unlike universal login, embedded authentication gives developers more control over the entire process by keeping the auth process and logic within your application’s domain. This approach provides greater flexibility and customization over the user interface, business logic, and event flow while interfacing with the the auth provider via SDK or API to handle secure authentication protocols.
Auth providers like Stytch offer client-side, server-side, and hybrid integrations options for embedded authentication, allowing you to tailor authentication to your application's specific codebase.
Pros and Cons: Side-by-Side
When deciding between embedded authentication and universal login, it’s important to evaluate how each approach impacts your application’s user experience, development process, and security posture.
The table below highlights the key pros and cons of both approaches, providing a high-level comparison across various technical aspects to help illustrate their differences.
Auth0 Universal Login | Stytch Embedded Auth | |
|---|---|---|
Hosting | ||
Hosting | Login page is hosted on an external, third-party domain. | Login page is self-hosted on your application’s domain. |
UX & UI | ||
UX & UI | Limited control over the design and UX. Users are redirected offsite to complete the auth flow. | Full code-control over the design and UX. Users stay within your application for the entire auth flow. |
Development Flexibility | ||
Development Flexibility | Limited flexibility. Relies on external dashboard-driven configuration and low-code flow builders. | Maximum flexibility. Offers native, granular code control over auth features and logic through SDKs and APIs. |
Setup | ||
Setup | Requires minimal development effort to set up but offers limited customization. | Requires upfront development effort but offers extensive customization. |
Security & Visibility | ||
Security & Visibility | Provides limited transparency into auth events, monitoring, data protection, compliance, etc. | Provides full visibility into auth events, monitoring, data protection, compliance, etc. |
Why Embedded Authentication Provides More Benefits
When choosing between embedded authentication and universal login, it's crucial to understand the aspects of each approach offers in-depth. Below, we’ll explore why embedded authentication stands out as the option with more benefits and why companies seeking optimal user experience, security, and developer flexibility should prioritize it over universal login.
Control Over the User Experience
For companies that value brand consistency, embedded authentication offers a significant advantage. By customizing the entire auth flow, you ensure that every interaction—whether it’s logging in, resetting a password, or signing up—stays within the familiar environment of your application. This results in a more seamless and tailored experience. In contrast, when configuring universal login, Auth0 forces you to use their external login pages, limiting your ability to fully customize the universal login experience.

A great example is Stytch’s customer, Apartment Therapy, who saw a 10x increase in user registrations after switching from a universal login provider to Stytch, an embedded auth provider. This demonstrates one of the key advantages of embedded authentication—users can complete the login flow without being redirected away from the app’s web pages, which results in a smoother experience and higher conversion rates for end users.
We moved from Auth0 to Stytch and implemented the Google OneTap method. Within a month, we saw a 10x increase in user registration and are now rolling this out across our other digital properties.
Development Control, Flexibility, & Customization
When it comes to development, Stytch embedded authentication provides a much greater degree of flexibility and code control. You can choose between client-side, server-side, or hybrid integrations to best fit your application’s architecture. Whether you're building web apps, mobile apps, single page applications, or more complex backend systems, Stytch’s SDKs and APIs give you full native code control over authentication logic, features, and security measures.
On the other hand, Auth0 universal login is largely controlled by a hosted dashboard-driven code builder known as “actions”, similar to lambdas or edge functions, which simplifies setup but severely limits the level of customization. Developers are constrained to using Auth0’s hosted rules, actions and configurations, making it harder to implement advanced use cases or extend custom logic specific to your application’s needs without workarounds.
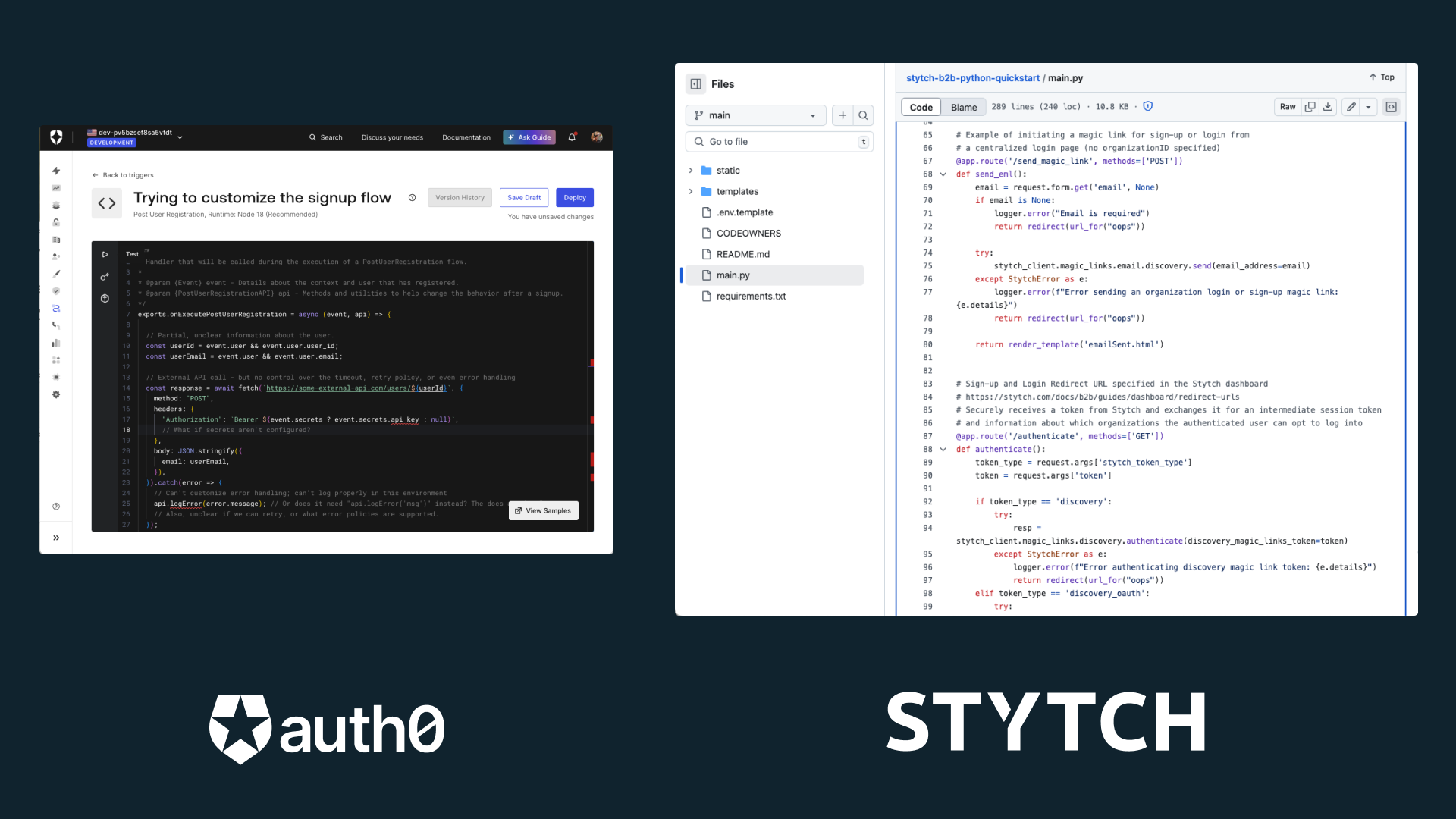
By deliberately housing custom logic solely within an external dashboard platform, Auth0 subjects developers to experience the following drawbacks:
- Limited code reusability - Auth0 actions are isolated and disparate functions, complicating code reuse and maintenance across your application.
- Fragmented version control - Actions can’t be managed within the main codebase, leading to version control inconsistencies and difficult application level changes.
- Auth0-specific limitations - Developers must navigate several Auth0-specific restrictions, such as limited runtime configurations, capped execution time, Node.js only, constraints on external API calls, and more.

Security and Visibility
Another major consideration for any authentication solution is security, and Stytch embedded authentication offers full visibility and control over security events, monitoring, and data protection. This is crucial for businesses that require transparency in how authentication flows are managed, especially when dealing with sensitive data or compliance requirements.
With Auth0 universal login, much of the security is outsourced to the provider. While this simplifies management, it also means you have little to no insight into critical security measures, relying on event log integrations with filtered data to monitor auth, including token handling, fraud detection, session management, and encryption protocols. This "black box" approach can be problematic for organizations that need granular control over their security posture and insight into how their user data is protected.
In contrast, with Stytch, your application logs are also your auth logs, providing direct, granular insight into every aspect of user security within your own environment.
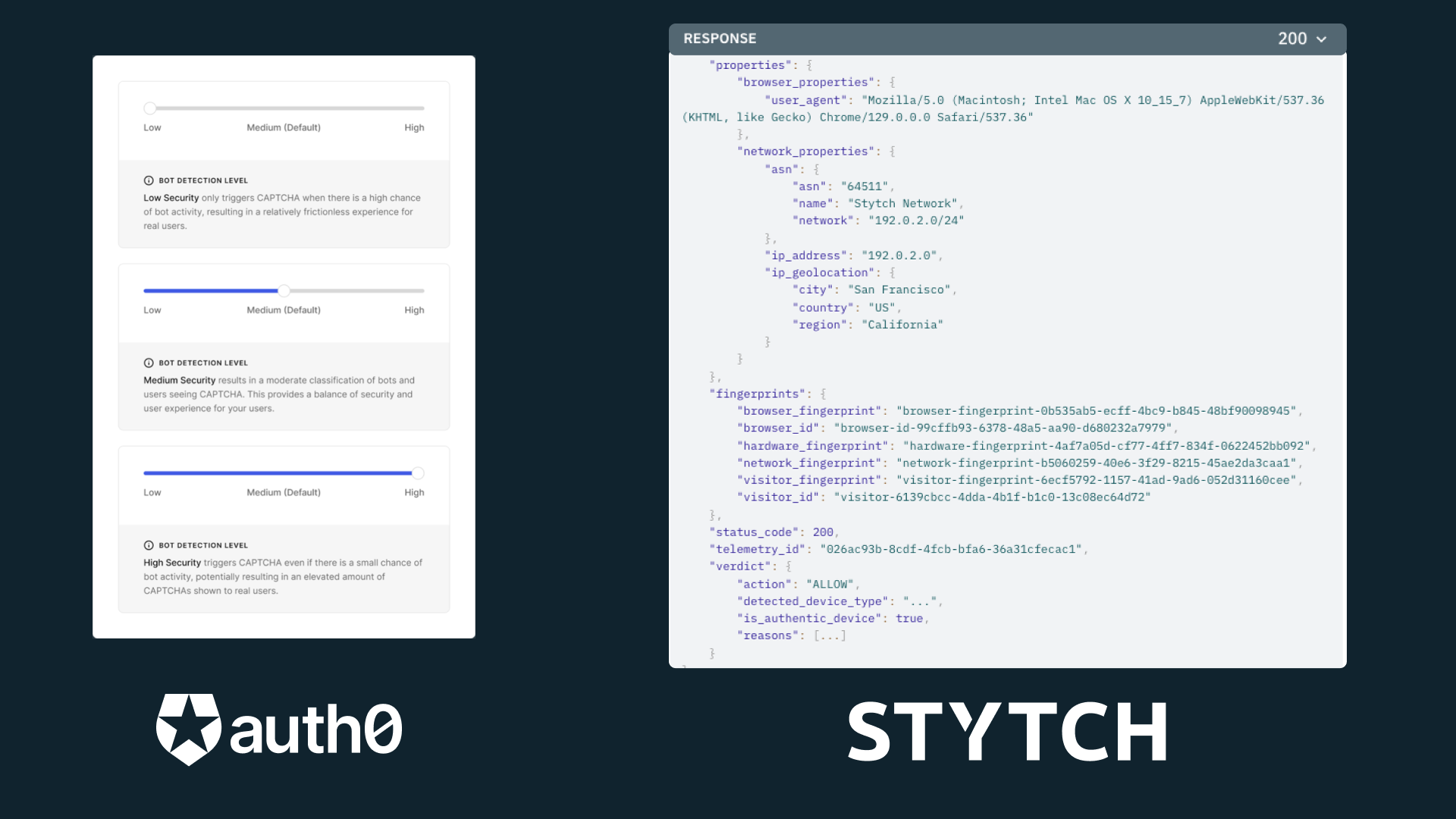
Universal login providers like Auth0 often push users toward their solutions, not just for convenience but out of necessity. Recurring vulnerabilities, such as the "alg: nonE" bug and recent authentication bypasses, reveal deeper issues in their security practices. These incidents highlight the need for a more proactive approach to safeguarding data.
While universal login might seem like a smart way to manage risks, it often sacrifices flexibility. Companies need security vendors that offer both strong protection and adaptable integration options, avoiding the rigidity of one-size-fits-all solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Embedded Authentication
How does embedded auth handle cross-origin requests?
Modern web applications provide effective solutions to mitigate the risks of cross-origin requests. By implementing Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) policies, you can control which domains are allowed to interact with your embedded authentication service. These policies ensure that only trusted domains are permitted to interact with the authentication service, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
How does embedded auth mitigate phishing attacks?
Embedded authentication can effectively mitigate the risk of phishing attacks with the right security measures in place. While some believe that using embedded login may expose applications to phishing risks due to multiple login pages across different sites, most businesses use a unified login page for their applications, which significantly reduces the number of sites this concern applies to.
But for applications with multiple login pages, a number of different strategies can mitigate this risk:
- Implementing a strong Content Security Policy (CSP): By explicitly defining trusted sources, you can block unapproved scripts and significantly reduce the chances of phishing attacks.
- Additional security measure: By integrating multi-factor authentication (MFA) or Device Fingerprinting Protected Authentication (DFP) into your authentication flow, you can greatly enhance security. These measures make it much more challenging for malicious actors to access accounts through phishing, social engineering, or other attack vectors, even when a user's password is compromised.
Stytch's SDKs also have many guardrails and javascript controls in place, such as trusted domains and trusted redirect URLs to protect the flow of information between your client and Stytch. With an embedded authentication provider, you also have the flexibility to integrate via backend APIs and SDKs, eliminating the cross-origin aspect entirely.
Does embedded auth add complexity to feature rollouts?
A key component of a universal login is a heavy reliance on dashboard-driven management for custom code and business logic. One perceived benefit of managing things like authentication methods and post-login logic through a dashboard is the ability to make changes in production quickly without a code release. However, this ease of use often comes at the expense of flexibility and the safety of robust version control.
Embedded authentication, on the other hand, typically offers a mix of in-code and dashboard configuration options, depending on where in your application stack authentication was integrated (e.g. backend or frontend). There are several advantages to this approach, namely:
- Version control for major changes: By managing configuration changes through in-code configs, your team will have a better grasp on version management and audit trails. This eliminates the possibility of a team member accidentally turning off a feature in production with the click of a mouse, with no ability to audit log how the incident occurred (we have heard of this happening many times from our customers!)
- More granular feature implementations: With embedded auth, you retain control over how you’d like to roll out a new feature when leveraging embedded authentication. Take for example enabling MFA. When auth settings are confined to a dashboard UI solution like with universal login, you may have access to “turn on” and “turn off” MFA, and potentially configure some additional settings. However, embedded authentication allows for much greater precision. You can define which user account you’d like to trigger MFA for or when it should be forced—whether at initial login or as step-up authentication when a user performs a sensitive action. This level of customization ensures that auth settings are tailored to your specific feature needs.
With embedded authentication, you can integrate advanced security protocols such as MFA and bot detection from the start within your codebase, preventing reactive disruptions that can negatively impact user experience.
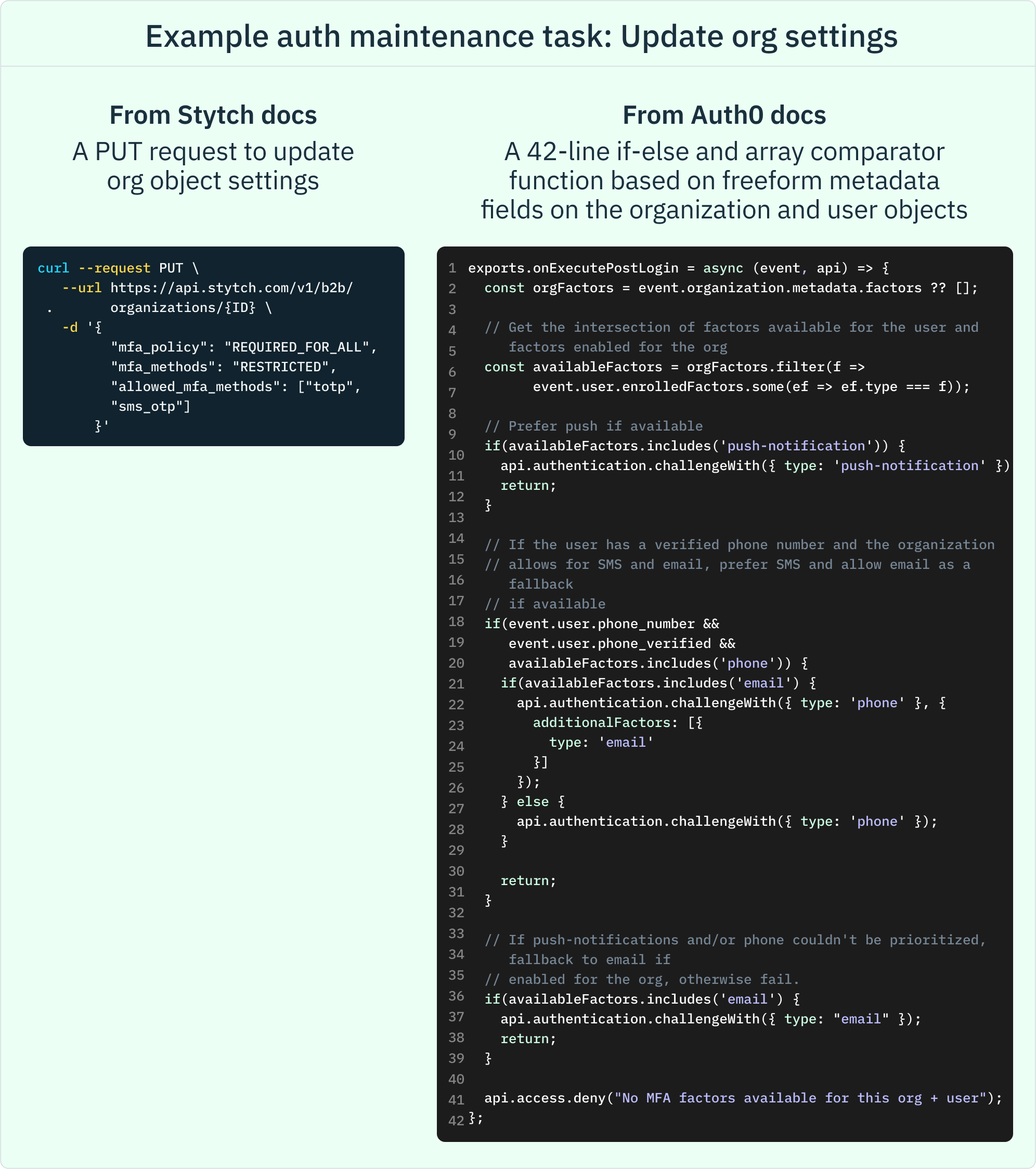
Ultimately, embedded authentication provides a balance between flexibility, security, and control, allowing you to roll out features in a way that aligns with your application’s specific integration work without compromising the user experience.
Does embedded auth support cross-domain sessions with OAuth 2.0?
Embedded authentication can indeed support cross-domain session sharing with OAuth 2.0 and OIDC redirects, making shareable access tokens across applications to prove a user's identity.
Stytch, as an embedded authentication provider, is currently testing its "Be the IdP" feature in a private beta. This feature enables a centralized login for all your applications, similar to social login, while preserving the core advantages of embedded authentication, such as a seamless user experience and full control over the UX. With this approach, you can enjoy the benefits of both centralized login and flexible, customized authentication.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between Stytch embedded authentication and Auth0 universal login boils down to your priorities in user experience, security, and control. Universal login is appealing for its simplicity and one-size-fits-all setup, but it imposes limitations on developer customization and control. Applications that adopt universal login often find themselves constrained by the lack of flexibility of hosted auth and dashboard-driven development.
Stytch's embedded authentication offers more benefits with more investment—seamless integration, full control, and proactive security measures that empower you to design the auth systems native to your application’s architecture. By keeping the authentication process embedded within your app, you not only improve conversion rates and user satisfaction, but also gain full control over security practices and business logic within your codebase.
Learn More
Learn more about how to migrate and integrate with an embedded authentication provider:
Build with Stytch
Pricing that scales with you • No feature gating • All of the auth solutions you need plus fraud & risk
Authentication & Authorization
Fraud & Risk Prevention
© 2025 Stytch. All rights reserved.


